Workflow¶
With a solid grounding in SpikeInterface, and a grasp of spikely’s element, parameter, and pipeline abstractions, the last piece of the puzzle to unlocking spikely’s potential is understanding its workflow and associated UI layout.
At a high level spikely’s workflow consists of creating a pipeline of elements, configuring the parameters associated with those elements, and finally, running the pipeline to cause extracellular data to be brought into the pipeline by the Extractor and transformed by the other elements in the pipeline flow.
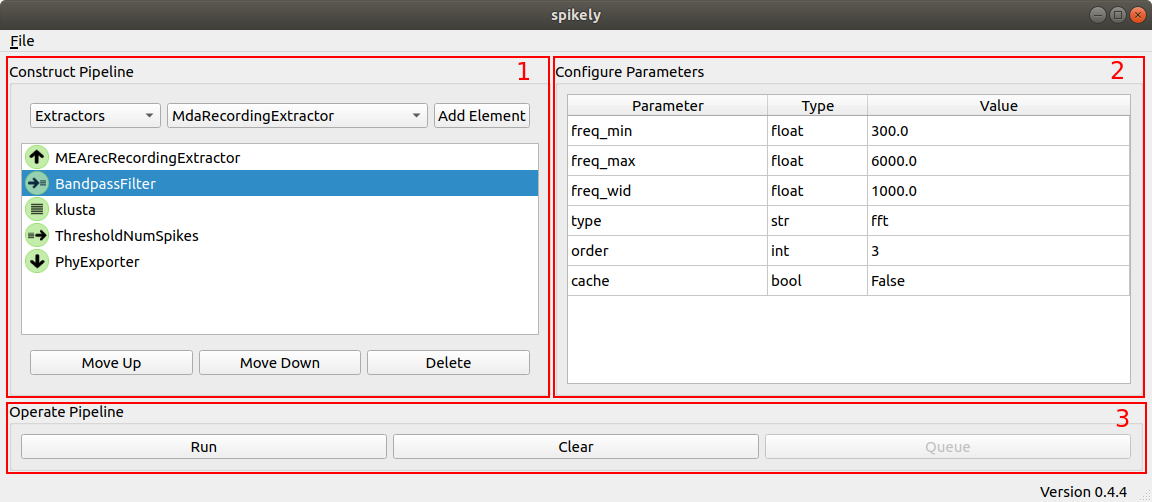
- Constructing the Pipeline - The user constructs a pipeline in spikely by choosing the element category (e.g., Extractors), choosing one of the installed elements within that category (e.g., MdaRecordingExtractor) and then adding that element to the pipeline using the “Add Element” button. Individual elements added to the pipeline can be moved up, moved down, or deleted as part of pipeline construction process. Note, there are pipeline policies enforced by spikely related to ordering and singularity that limit certain pipeline permutations.
- Configuring Element Parameters - When an element is selected in the Construct Pipeline part of the UI that element’s parameters are displayed in the Configure Elements part of the UI. Element parameters are specific to it, so a detailed explanation of an element’s parameters will need to be gleaned from the corresponding SpikeInterface documentation. Clicking on the Value field for a parameter enables the user to edit it. Spikely does rudimentary type checking, but for the most part it is up to the user to ensure that a parameter value is valid.
- Operating the Pipeline - While the commands available to the user in the Construct Pipeline’ part of the UI operate on individual elements in the pipeline, *Operate Pipeline commands act on the pipeline as a whole. Currently, two operations are supported: Run, and Clear. Clear deletes all the elements in the pipeline enabling the user to quickly tear down the current pipeline before building up a new one. Run is where the magic happens, instantiating the pipeline and transforming the extracellular data as it flows from the source element (Extractor) to the sink element (Sorter or Exporter).
Tip
The pipeline creation and parameter configuration steps can be shortcut by saving and loading complete pipelines to/from files using the corresponding actions from spikely’s File Menu.